Status
Development
Support
- 京ICP备2025123107号-1
- Worker 0, 65ms
- Powered by Hydro v5.0.0-beta.15 Community
N 皇后问题是一个经典的回溯算法问题,要求在一个 n × n 的棋盘上放置 n 个皇后,确保没有两个皇后能相互攻击。根据国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击同行、同列、同斜线上的棋子,因此我们需要确保在摆放皇后时,满足以下条件:
按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。
n皇后问题研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
输入只有一行,包含一个整数 n。
输出所有不同的解决方案,每个方案占 n 行,每行有 n 个字符('Q' 或 '.'),方案之间用一个空行分隔。
注意:方案的输出顺序不限,但每个方案内部的行顺序必须严格从上到下。
输入
4
输出
.Q..
...Q
Q...
..Q.
..Q.
Q...
...Q
.Q..
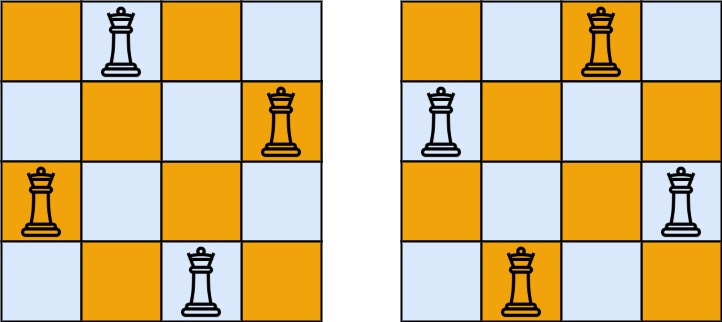
如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
输入
1
输出
Q
提示: