Status
Development
Support
- 京ICP备2025123107号-1
- Worker 2, 70ms
- Powered by Hydro v5.0.0-beta.15 Community
本题要求对一个单链表进行升序排序,属于经典链表排序问题。
链表不支持随机访问,因此不能直接使用快速排序等数组常用的排序算法。
对于链表排序,常用且高效的方法是『归并排序』:
给你链表的头结点 head,请将其按 升序 排列并输出 排序后的链表 。
输入共一行,包含若干个整数,以空格隔开,表示链表节点的值。
输出共一行,包含排序后链表节点的值,用空格隔开。
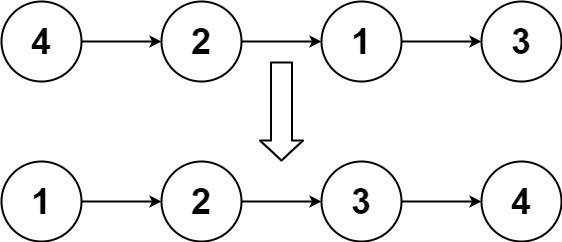
输入
4 2 1 3
输出
1 2 3 4

输入
-1 5 3 4 0
输出
1 2 3 4